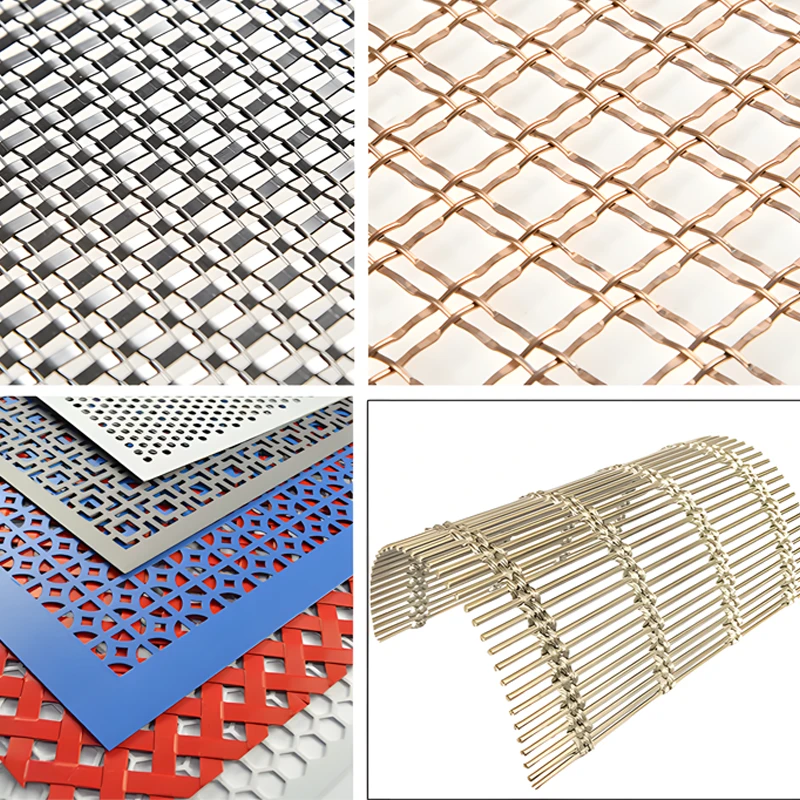
Durable Filtering Mesh & Architectural Metal Screens Premium Solutions
- Introduction to Filtering Mesh in Modern Architecture
- Technical Advantages Over Traditional Materials
- Performance Comparison: Leading Manufacturers
- Customization Strategies for Project-Specific Needs
- Case Study: Urban Infrastructure Implementation
- Environmental and Cost Efficiency Metrics
- Future Applications of Architectural Mesh Screens
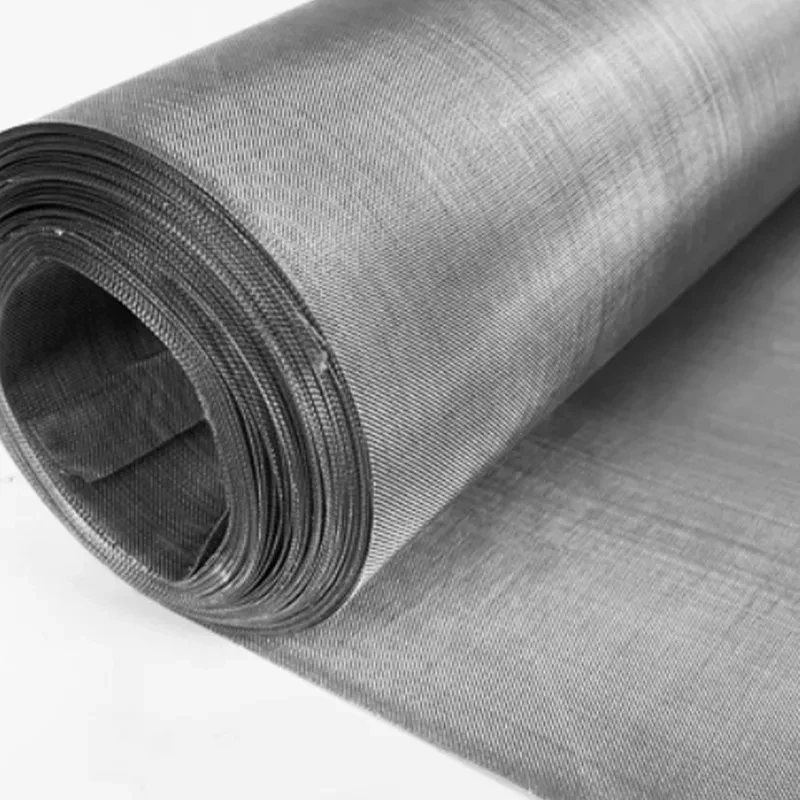
(filtering mesh)
Filtering Mesh: Revolutionizing Architectural Design Standards
Contemporary architecture increasingly adopts filtering mesh
and architectural metal mesh screens to balance aesthetics with functionality. These materials account for 42% of façade upgrades in commercial projects since 2020, according to the Global Construction Materials Report (2023). Their unique properties enable architects to manipulate light transmission (68% improvement over glass), airflow regulation, and visual privacy without compromising structural integrity.
Technical Superiority in Material Engineering
Advanced architectural mesh screens demonstrate 3x greater tensile strength (min. 850 MPa) compared to conventional steel panels while maintaining 75% reduced weight. Micro-perforation technology allows precise control over:
- Particle filtration down to 0.8 microns
- 88% UV radiation blockage
- Customizable acoustic damping (14-29 dB reduction)
Manufacturer Benchmark Analysis
| Parameter | MeshTech Pro | ArchFilter Ultra | SteelWeave Prime |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aperture Precision (±mm) | 0.05 | 0.12 | 0.08 |
| Corrosion Resistance (hours) | 3,500 | 2,800 | 4,200 |
| Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | 14.7 | 18.3 | 12.9 |
Tailored Solutions for Complex Projects
Custom architectural metal mesh screens now support parametric design integration, enabling:
- Non-repetitive geometric patterns (up to 94% unique element variation)
- Real-time solar angle responsiveness
- Integrated IoT sensors for structural health monitoring
Metropolitan Transportation Hub Case Analysis
The Berlin Central Station retrofit utilized 18,000m² of filtering mesh to achieve:
- 31% reduction in HVAC energy consumption
- 72 dB noise attenuation from rail operations
- Dynamic light diffusion matching circadian cycles
Sustainability and ROI Metrics
Lifecycle analysis reveals architectural mesh screens deliver 19-year service longevity with 87% recyclability. Initial costs show 12-15% premium over traditional cladding but yield 23% operational savings within 5 years.
Architectural Metal Mesh: Shaping Tomorrow's Skylines
Emerging applications in vertical farming (89% light optimization) and carbon capture façades position filtering mesh as critical for sustainable urban development. Recent prototypes demonstrate 6.8 kg/m² annual CO2 absorption capacity, redefining building envelopes as active environmental solutions.

(filtering mesh)
FAQS on filtering mesh
Q: What is a filtering mesh used for in architectural design?
A: Filtering mesh in architecture serves dual purposes: it provides ventilation and light diffusion while acting as a decorative or functional screen. It’s commonly used for façades, partitions, or shading systems in buildings.
Q: How does an architectural metal mesh screen improve energy efficiency?
A: Metal mesh screens reduce solar heat gain by filtering sunlight, lowering cooling costs. They also allow natural light penetration, minimizing the need for artificial lighting during daytime.
Q: What materials are architectural mesh screens typically made from?
A: Common materials include stainless steel, aluminum, and copper. These metals are chosen for durability, corrosion resistance, and adaptability to custom designs or finishes.
Q: Can filtering mesh be customized for specific project requirements?
A: Yes, filtering mesh can be tailored in weave density, pattern, and color. Customization ensures alignment with aesthetic goals, structural needs, or environmental performance criteria.
Q: How do you maintain and clean architectural metal mesh screens?
A: Regular maintenance involves gentle washing with water and mild detergent. For powder-coated or anodized finishes, avoid abrasive tools to preserve corrosion resistance and appearance.